
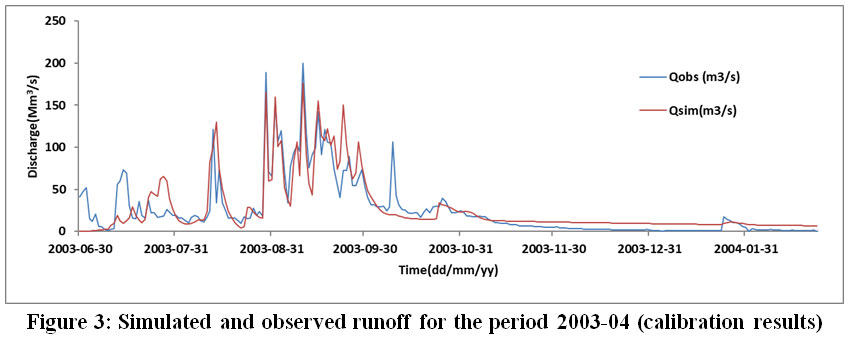

Calibration and validation of HL-RDHM were conducted using four-year data set each. For a one year period with the best precipitation data, the performance of HL-RDHM was satisfactory even without calibration for basin-averaged and distributed a priori parameter grids. More realistic rainfall and more accurate streamflow predictions were obtained with the ½ and ¼ HRAP grids. Hourly basin-average rainfall calculated from one HRAP resolution grid (4 km × 4 km) was too low and inaccurate. Results were obtained for several spatial resolutions. Application of HL-RDHM to Hanalei watershed required (i) modifying the Hydrologic Rainfall Analysis Project (HRAP) coordinate system (ii) generating precipitation grids from rain gauge data, and (iii) generating parameters for Sacramento Soil Moisture Accounting Model (SAC-SMA) and routing parameter grids for the modified HRAP coordinate system. This rural watershed is very wet and has strong spatial rainfall gradients. Motivated by the possibility of developing an operational flood forecasting system, this study evaluated the performance of the National Weather Service (NWS) model, the Hydrology Laboratory Research Distributed Hydrologic Model (HL-RDHM) in simulating the hydrology of the flood-prone Hanalei watershed in Kaua‘i, Hawai‘i. Many watersheds in Hawai‘i are flash flood prone due to their small contributing areas and frequent intense rainfall.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
